The OWASP Top 10 security risks for PHP applications
Nic Wortel
@nicwortel
About me
- Independent software consultant and trainer
- PHP, Symfony, DDD, CI/CD, Docker, Kubernetes
- Reservist at Royal Dutch Army
Raise your hand if
You have ever found a security vulnerability in the software you work on
Raise your hand if
The software you work on has had a data breach
Raise your hand if
Your personal data has been part of a data breach
Why care?
$4.24 million
Was the average cost of a data breach in 2021
$161 per record
Was the average cost per record of a data breach
€ 10 million or 2% of annual global turnover
(whichever is higher) maximum GDPR fine for insufficiently protecting data, or not reporting a data breach in time.
Source: GDPR Fines
As engineers, we have an ethical obligation to deliver secure software
...and can be legally held responsible for what we develop
OWASP
The Open Web Application Security Project
OWASP projects
The OWASP Top 10
The OWASP Top 10 is a standard awareness document for developers and web application security. It represents a broad consensus about the most critical security risks to web applications.
OWASP Top 10 2017
- Injection
- Broken Authentication
- Sensitive Data Exposure
- XML External Entities (XXE)
- Broken Access Control
- Security Misconfiguration
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
- Insecure Deserialization
- Using Components with Known Vulnerabilities
- Insufficient Logging & Monitoring
OWASP Top 10 2021
- Broken Access Control
- Cryptographic Failures
- Injection
- Insecure Design
- Security Misconfiguration
- Vulnerable and Outdated Components
- Identification and Authentication Failures
- Software and Data Integrity Failures
- Security Logging and Monitoring Failures
- Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF)
1. Broken Access Control

Common weaknesses
- Exposure of Sensitive Information to an Unauthorized Actor
- Insertion of Sensitive Information Into Sent Data
- Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF)
Example scenarios
Changing an identifier in the URL to view someone else's account information
$stmt = $pdo->prepare('SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = :id');
$stmt->execute(['id' => $_GET['id']]);
$user = $stmt->fetch();
Example scenarios
Cross-Site Request Forgery
Prevention
Except for public resources, deny by default.
Symfony and Laravel by default allow all access.
In Symfony consider creating a catch-all URL pattern to deny access to URLs without explicit access control.
Implement access control mechanisms once and re-use them throughout the application
Model access controls should enforce record ownership rather than accepting that the user can create, read, update, or delete any record.
// Using Symfony Voter
$this->denyAccessUnlessGranted('view', $profile);
// Using Laravel Policy
if (!Gate::allows('view', $profile))
Unique application business limit requirements should be enforced by domain models.
public function addProduct(
Product $product,
int $quantity
): void {
if ($quantity < 1) {
throw new MinimumQuantityException();
}
// $this->products[] = ...
}
Disable web server directory listing and ensure file metadata (e.g., .git) and backup files are not present within web roots.
# Apache
Options -Indexes
# Nginx (off by default)
autoindex off
Log access control failures, alert admins when appropriate (e.g., repeated failures).
$logger->error('Access denied');
Rate limit API and controller access to minimize the harm from automated attack tooling.
Symfony Rate Limiter component, Laravel RateLimiter
Stateful session identifiers should be invalidated on the server after logout. Stateless JWT tokens should rather be short-lived so that the window of opportunity for an attacker is minimized. For longer lived JWTs it's highly recommended to follow the OAuth standards to revoke access.
2. Cryptographic Failures

Common weaknesses
- Use of Hard-coded Password
- Broken or Risky Crypto Algorithm
- Insufficient Entropy
Example scenarios
- Intercepting and/or modifying unencrypted HTTP traffic (MitM) to steal sensitive data, inject keyloggers, etc.
- Using rainbow tables or brute-force attacks to reverse unsalted or weakly hashed passwords.
Prevention
Classify data processed, stored, or transmitted by an application. Identify which data is sensitive according to privacy laws, regulatory requirements, or business needs.
For example: GDPR
Don't store sensitive data unnecessarily. (...) Data that is not retained cannot be stolen.
Make sure to encrypt all sensitive data at rest.
Use the Sodium extension and Halite.
use ParagonIE\Halite\KeyFactory;
use ParagonIE\Halite\Symmetric\Crypto as Symmetric;
use ParagonIE\HiddenString\HiddenString;
$encryptionKey = KeyFactory::loadEncryptionKey($path);
$message = new HiddenString('Secret message');
$ciphertext = Symmetric::encrypt($message, $encryptionKey);
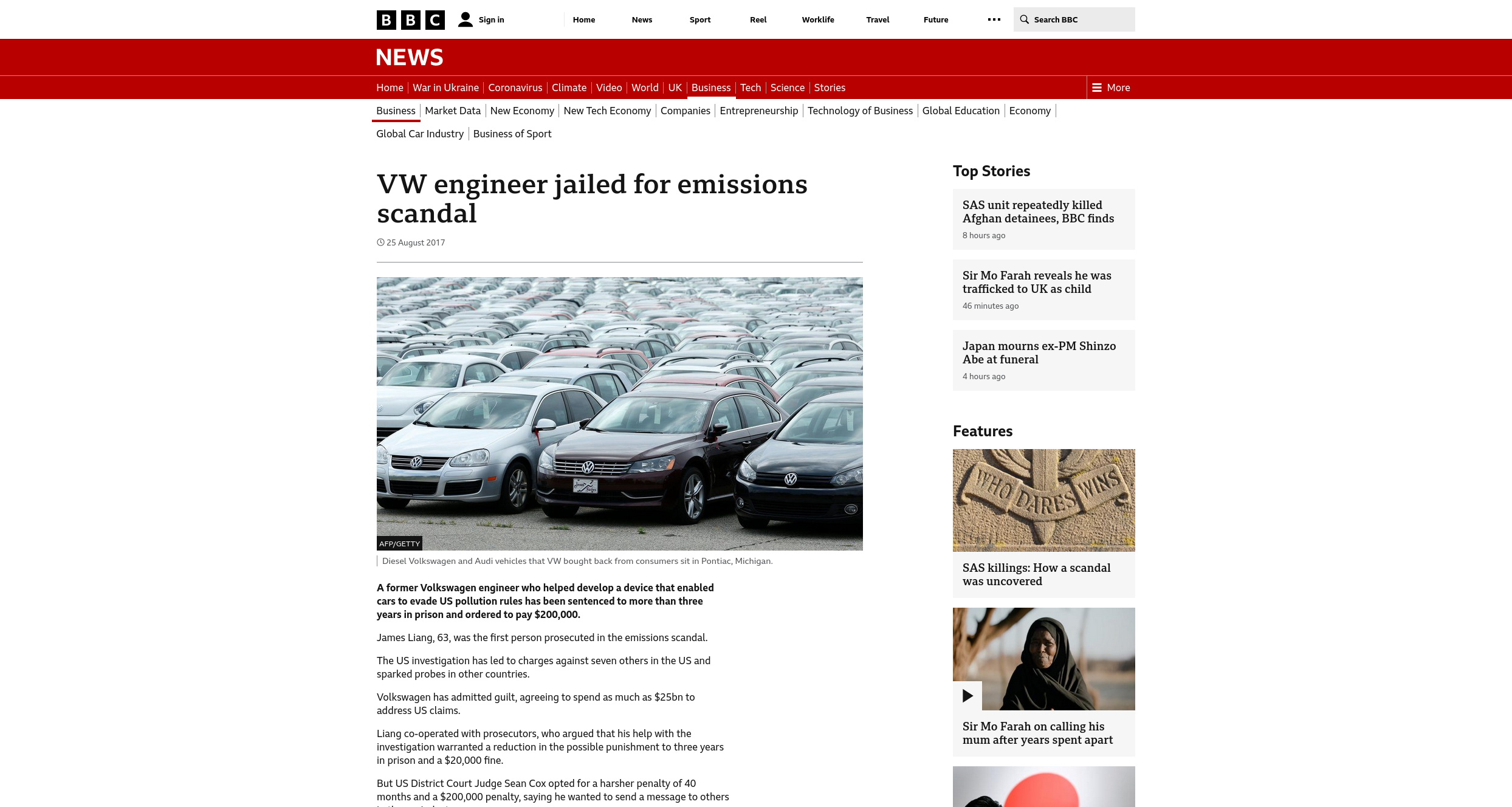
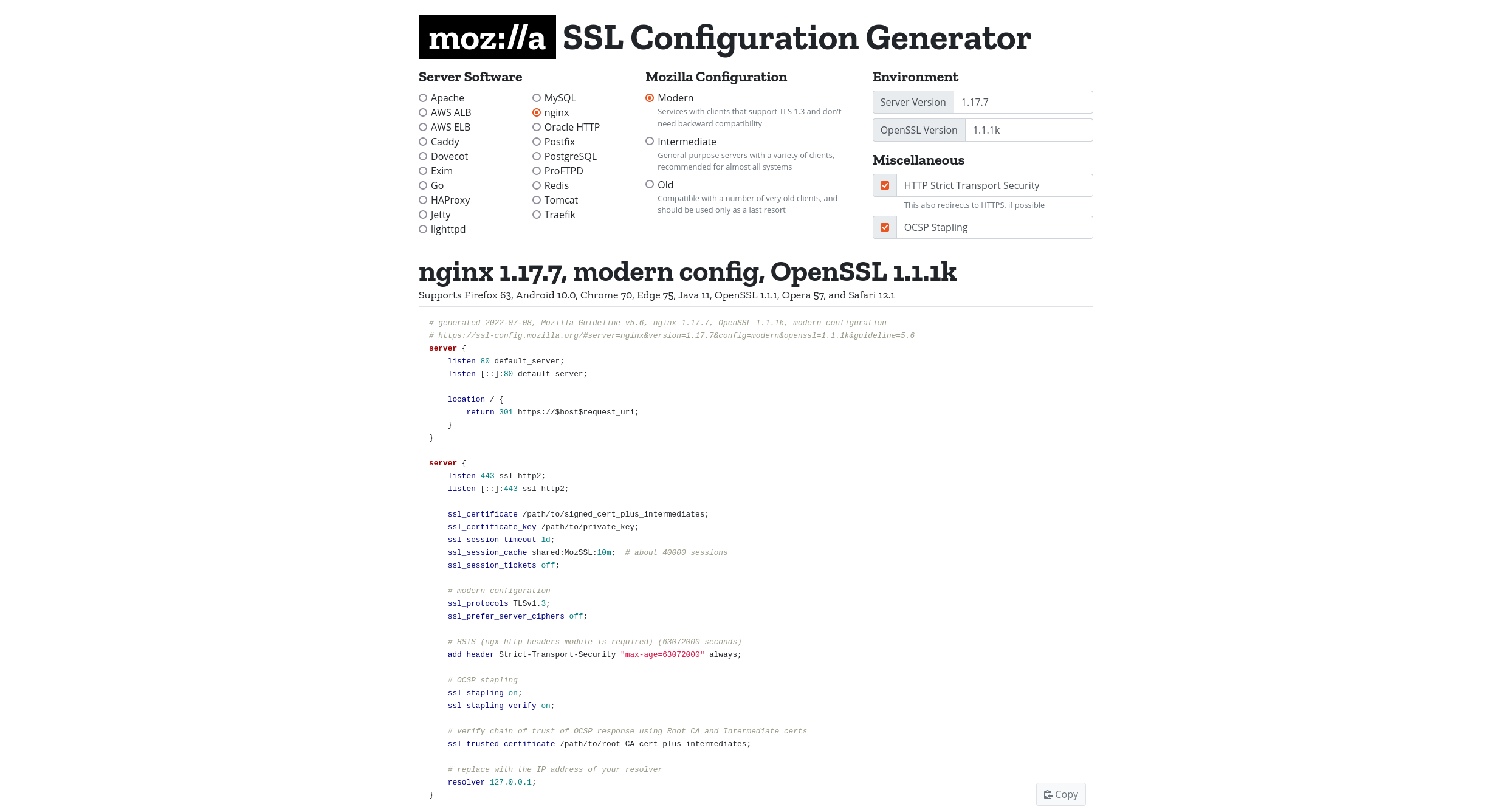
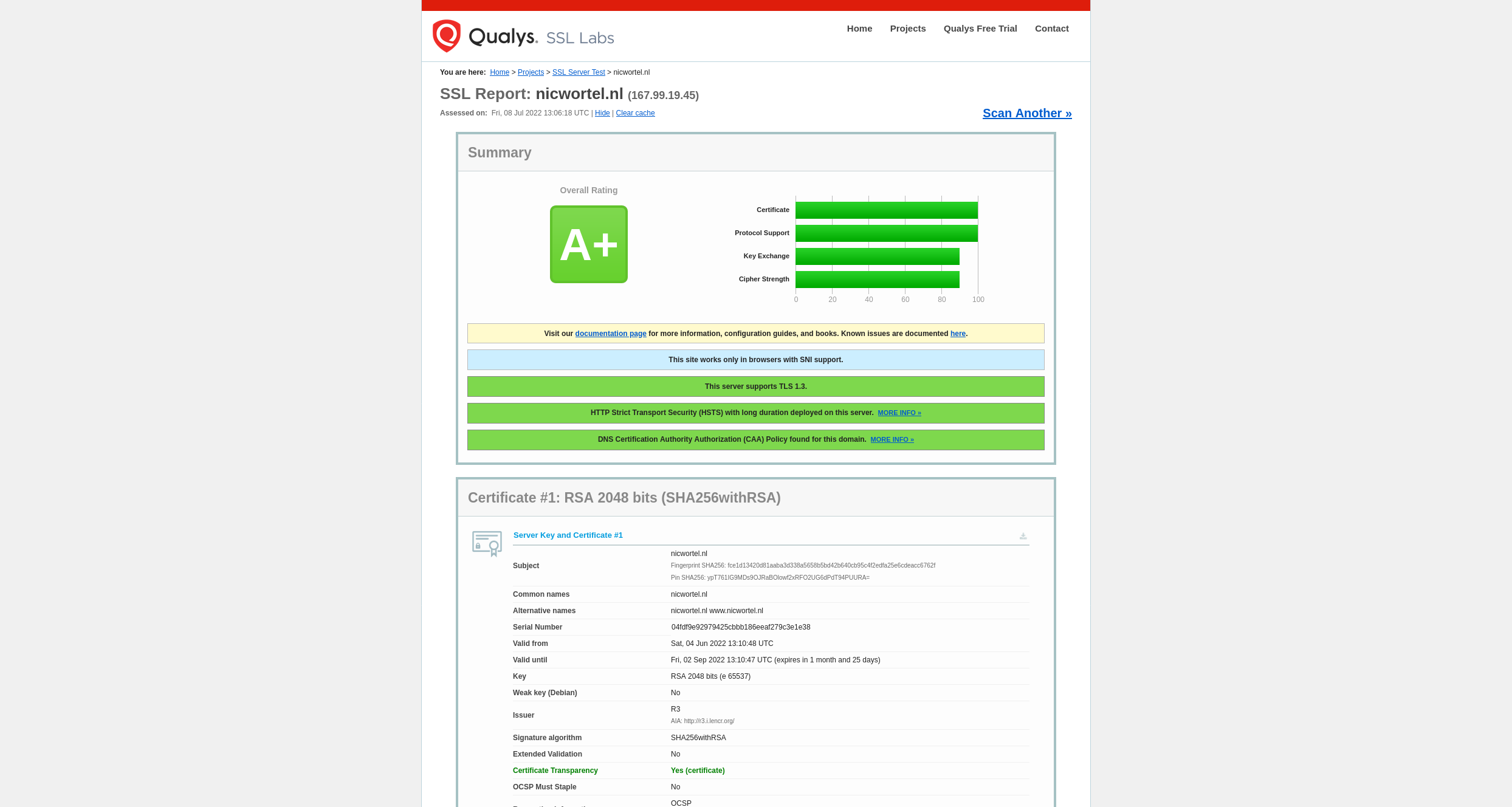
Encrypt all data in transit with secure protocols such as TLS with forward secrecy (FS) ciphers, cipher prioritization by the server, and secure parameters. Enforce encryption using directives like HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS).
Use the Mozilla SSL Configuration Generator and Qualys SSL Server Test to generate and verify server configuration.
Disable caching for response that contain sensitive data.
header("Cache-Control: no-store, no-cache, must-revalidate");
Store passwords using strong adaptive and salted hashing functions with a work factor (delay factor), such as Argon2, scrypt, bcrypt or PBKDF2.
$hash = password_hash('mysecretpassword', PASSWORD_DEFAULT);
Symfony "auto" Hasher
Laravel Hash facade
Initialization vectors must be chosen appropriate for the mode of operation. For many modes, this means using a CSPRNG (cryptographically secure pseudo random number generator) (...)
Use random_bytes() or random_int().
Use Halite.
Always use authenticated encryption instead of just encryption.
Use Halite...
Keys should be generated cryptographically randomly and stored in memory as byte arrays. If a password is used, then it must be converted to a key via an appropriate password base key derivation function.
Use Halite
Avoid deprecated cryptographic functions and padding schemes, such as MD5, SHA1, PKCS number 1 v1.5.
<element key="md5" value="null"/>
<element key="sha1" value="null"/>
3. Injection

Common weaknesses
- SQL injection
- OS command injection
- LDAP injection
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
- Eval injection
Example scenarios
$query = "SELECT id, name
FROM users
ORDER BY name
LIMIT 20
OFFSET " . $_GET['offset'];
$result = $connection->query($query);
Example scenarios
echo 'Hello, ' . $_GET['name'] . '
';
Prevention
(...) use a safe API, which avoids using the interpreter entirely, provides a parameterized interface, or migrates to Object Relational Mapping Tools (ORMs).
$stmt = $db->prepare('SELECT id, name (...) OFFSET :offset');
$stmt->bindParam(':offset', $offset);
$stmt->execute();
Use positive server-side input validation.
For any residual dynamic queries, escape special characters using the specific escape syntax for that interpreter.
# PDO
$pdo->quote($input);
# LDAP
ldap_escape($input);
# Symfony LDAP
$ldap->escape($input);
Avoid passing user imput to PHP functions that execute commands on the server:
exec()shell_exec()passthru()system()
Use the Symfony Process component instead
Avoid the use of eval()
<element key="eval" value="null"/>
Use a template engine with XSS protection (Twig, Blade, etc.)
Be very careful when disabling XSS protection:
{{ variable|raw }}
4. Insecure Design

Example scenarios
An application is vulnerable not because of implementation flaws, but due to design and architectural flaws.
Prevention
Establish and use a secure development lifecycle with AppSec professionals to help evaluate and design security and privacy-related controls
Establish and use a library of secure design patterns or paved road ready to use components
Follow the Symfony security best practices
Use threat modeling for critical authentication, access control, business logic, and key flows
See OWASP SAMM: Threat Assessment & Threat Modeling Manifesto
Integrate security language and controls into user stories
Write unit and integration tests to validate that all critical flows are resistant to the threat model. Compile use-cases and misuse-cases for each tier of your application.
Test security logic using PHPUnit and/or Behat.
5. Security Misconfiguration

Common weaknesses
- Configuration
- Improper Restriction of XML External Entity Reference
Example scenarios
- Attackers scanning for MongoDB installations not protected by a password, stealing data and demanding ransom.
- Applications displaying detailed error messages (stack traces) to users, which can be used to expose sensitive information or underlying flaws.
Prevention
A repeatable hardening process makes it fast and easy to deploy another environment that is appropriately locked down.
Create reproducible environments using Docker and/or tools such as Ansible.
Configure PHP to not expose detailed error messages or version information:
expose_php = off
display_errors = off
Limit which directories can be accessed through functions like include() and fopen():
open_basedir = "/var/www/html/"
A minimal platform without any unnecessary features, components, documentation, and samples. Remove or do not install unused features and frameworks.
Disable unneeded PHP extensions, features and functions
allow_url_fopen = off
disable_functions = exec,passthru,shell_exec,system,eval
A task to review and update the configurations appropriate to all security notes, updates, and patches as part of the patch management process. Review cloud storage permissions (e.g., S3 bucket permissions).
A segmented application architecture provides effective and secure separation between components or tenants, with segmentation, containerization, or cloud security groups (ACLs).

Sending security directives to clients, e.g., Security Headers.
Configure your web server or application to send security headers such as:
- Strict-Transport-Security (HSTS)
- Content-Security-Policy (CSP)
- X-Frame-Options
- Referrer-Policy
Set your Content-Security-Policy to deny by default and whitelist specific sources used by your application.
Configure a report-uri (for example using report-uri.com) and monitor CSP violations.
Useful packages:
- NelmioSecurityBundle (Symfony)
- bepsvpt/secure-headers (Laravel)
- paragonie/csp-builder
Use Mozilla Observatory and Security Headers to verify your security headers.
6. Vulnerable and Outdated Components

Example scenarios
- Log4Shell
- Vulnerabilities in Composer packages
- Vulnerabilities in PHP versions
Prevention
Remove unused dependencies, unnecessary features, components, files, and documentation.
phive install -g composer-unused
composer-unused
Continuously inventory the versions of both client-side and server-side components and their dependencies
Use the Local PHP Security Checker to check against the PHP Security Advisories Database.
Monitor for libraries and components that are unmaintained or do not create security patches for older versions.
composer outdated
7. Identification and Authentication Failures

Common weaknesses
- Improper Validation of Certificate with Host Mismatch
- Improper Authentication
- Session Fixation
Example scenarios
- An attacker can perform credential stuffing (trying out thousands of passwords from a data breach somewhere else) without being throttled.
- Sessions remain valid too long, allowing someone on a public computer to continue the session of a user who closed the browser without logging out.
Prevention
Where possible, implement multi-factor authentication to prevent automated credential stuffing, brute force, and stolen credential reuse attacks.
Symfony SchebTwoFactorBundle, Laravel Fortify, or similar
Do not ship or deploy with any default credentials, particularly for admin users.
Implement weak password checks, such as testing new or changed passwords against the top 10,000 worst passwords list.
Check passwords against exposed passwords from the Have I Been Pwned password database.
Use the NotCompromisedPassword validation constraint in Symfony.
namespace App\Entity;
use Symfony\Component\Validator\Constraints as Assert;
class User
{
#[Assert\NotCompromisedPassword]
protected $rawPassword;
}
In Laravel you can use valorin/pwned-validator
Align password length, complexity, and rotation policies with National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) 800-63b's guidelines in section 5.1.1 for Memorized Secrets or other modern, evidence-based password policies.
- min. 8 characters
- allow at least 64 characters or longer
- don't store password hints
- reject compromised / expected passwords
- don't require a mix of character types
- don't require periodical changing
Ensure registration, credential recovery, and API pathways are hardened against account enumeration attacks by using the same messages for all outcomes.
Limit or increasingly delay failed login attempts, but be careful not to create a denial of service scenario. Log all failures and alert administrators when credential stuffing, brute force, or other attacks are detected.
Laravel Breeze and Jetstream starter kits come with Login Throttling based on the RateLimiter.
For Symfony you can use LoginGateBundle.
Use a server-side, secure, built-in session manager that generates a new random session ID with high entropy after login. Session identifier should not be in the URL, be securely stored, and invalidated after logout, idle, and absolute timeouts.
Let the framework handle sessions for you.
8. Software and Data Integrity Failures

Common weaknesses
- Inclusion of Functionality from Untrusted Control Sphere
- Download of Code Without Integrity Check
- Deserialization of Untrusted Data
Example scenarios
- Passing a crafted string to an application which uses
deserialize()to deserialize it, allowing remote code execution.
Prevention
Use digital signatures or similar mechanisms to verify the software or data is from the expected source and has not been altered.
Sign your Git commits
Use digital signing to verify data coming from an untrusted source (the request)
Ensure libraries and dependencies, such as npm or Maven, are consuming trusted repositories. If you have a higher risk profile, consider hosting an internal known-good repository that's vetted.
Ensure that a software supply chain security tool, such as OWASP Dependency Check or OWASP CycloneDX, is used to verify that components do not contain known vulnerabilities
Use the Local PHP Security Checker.
Ensure that there is a review process for code and configuration changes to minimize the chance that malicious code or configuration could be introduced into your software pipeline.
Do pair programming or code reviews
Don't use deserialize() on user-provided data
9. Security Logging and Monitoring Failures

Common weaknesses
- Insufficient Logging
- Improper Output Neutralization for Logs
- Omission of Security-relevant Information
- Insertion of Sensitive Information into Log File
Example scenarios
- Not detecting an attack or data breach due to a lack of logging and monitoring, so that attackers can continue to harvest data
Prevention
Ensure all login, access control, and server-side input validation failures can be logged with sufficient user context to identify suspicious or malicious accounts and held for enough time to allow delayed forensic analysis.
Use Monolog to log significant events to a centralized logging solution (ELK / Datadog / etc.)
Ensure that logs are generated in a format that log management solutions can easily consume.
Ensure log data is encoded correctly to prevent injections or attacks on the logging or monitoring systems.
Ensure high-value transactions have an audit trail with integrity controls to prevent tampering or deletion, such as append-only database tables or similar.
DevSecOps teams should establish effective monitoring and alerting such that suspicious activities are detected and responded to quickly.
Establish or adopt an incident response and recovery plan, such as National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) 800-61r2 or later.
10. Server-Side Request Forgery
Example scenarios
$content = file_get_contents($_GET['url']);
header("Content-Type: image/png");
echo $content;
https://example.com/img.php?url=http://internal.example.com/
Prevention
Sanitize and validate all client-supplied input data
Enforce the URL schema, port, and destination with a positive allow list
Do not send raw responses to clients
What's next?
The OWASP Top 10 is just a starting point
OWASP Top Ten Proactive Controls
The most important control categories that every architect and developer should absolutely, 100% include in every project.
OWASP ASVS
Application Security Verification Standard:
a verifiable and tested security standard